Millions of individuals worldwide suffer from the complexities of diabetes and its complications. Among these complications, diabetic foot stands out as a significant concern, leading to profound disability and, in extreme cases, necessitating amputation. Understanding why they occur, managing them effectively, and taking preventive measures are important steps in diabetic care.
This blog highlighted diabetic foot wounds – associated risk factors, symptoms and prevention care.
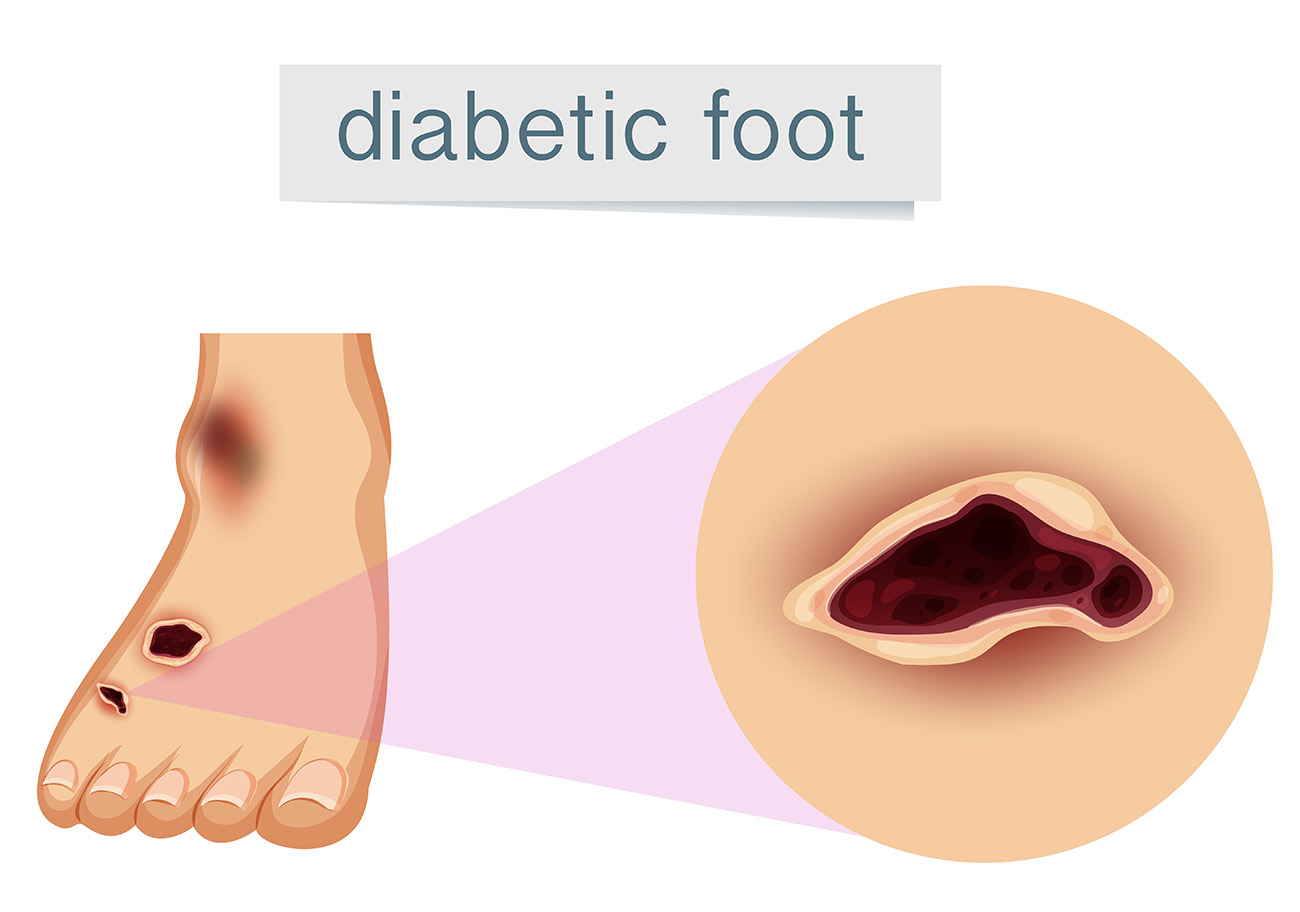
A foot wound in a diabetic person refers to any injury or break in the skin on the foot. This can include cuts, blisters, or abrasions. Foot wounds can occur due to various reasons, such as poor circulation, and nerve damage (neuropathy).
Why do diabetic people encounter foot wounds? This is one of the most commonly asked questions among diabetic people.
This is because diabetes can lead to nerve damage and poor blood circulation in the feet, making them more vulnerable to injuries and slower to heal. Therefore, those with diabetes need to take extra care of their feet to prevent wounds and complications.
If left unattended, diabetic foot wounds can progress into foot ulcers, commonly known as diabetic foot sores. How can you recognize a diabetic foot sore?
Initially, it may resemble a blister or burn. Approximately 20-25% of individuals with diabetes will experience a foot ulcer at some stage in their lives.
Consulting with a dietitian experienced in crafting healthy, nutritious, and flavorful meals for diabetics is strongly advised for diabetic foot care. Meals should be rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while avoiding foods high in calories and saturated fats.
In addition to dietary adjustments, bring physical exercise into daily routines. Physical activity can enhance circulation, potentially increasing oxygenation and nutrient delivery to wound sites. Weight loss may also improve glycemic control in individuals with obesity-related diabetes.
Diabetic foot treatment involves proper education to keep them in check. These wounds happen due to nerve damage, poor blood flow, and foot problems, raising the risk of serious issues like infections and amputations. Regular foot care—like checking your feet every day, wearing the right shoes, and seeing your healthcare provider—is key to preventing problems. Also, managing your blood sugar levels through healthy eating, exercise, and medication helps lower the chances of foot wounds. By staying aware, taking action early, and getting support from your healthcare team, you can keep diabetic foot issues at bay and enjoy better health.