In the realm of health management, understanding and conquering challenges can become powerful catalysts. Type 2 diabetes could be a common condition due to high blood sugar levels. In this blog, we delve into what exactly is type 2 diabetes, its symptoms, and most importantly, how to manage it effectively. Seek guidance from the best diabetes hospital in Coimbatore for in-depth insight on type 2 diabetes.
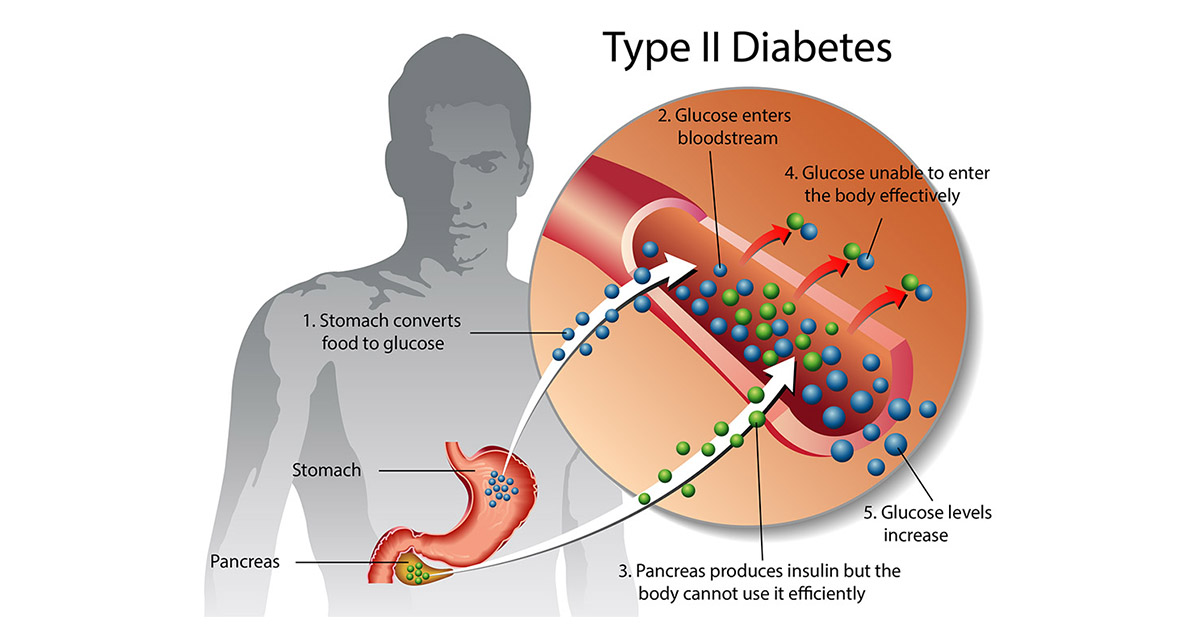
Type 2 diabetes, often known as adult-onset diabetes, arises when the body fails to generate enough insulin or becomes resistant to the insulin that is produced. Insulin is a hormone that controls blood sugar (glucose) levels and allows cells to use glucose for energy. Without normal insulin function, glucose accumulates in the circulation, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
Insulin, produced by the pancreas, acts as a key, allowing cells to use blood sugar for energy. In type 2 diabetes, cells resist insulin, resulting in high blood sugar levels. The pancreas increases insulin production but becomes overwhelmed, leading to prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar level affects the body, causing difficulties with the heart, eyes, and kidneys. Managing blood sugar is necessary to avoid these consequences and improve well-being.
Type 2 diabetes inheritance is not definite, but many individuals have at least one close family member, increasing the likelihood of developing the condition.
Excess body weight, particularly around the abdominal area, means you are more likely to have fatty tissue, which can increase the chance of insulin resistance.
Leading a sedentary lifestyle reduces the body’s sensitivity to insulin. Regular physical exercise improves your cells' response to insulin.
Processed food may contain a lot of refined sugar and hidden carbs.
Early identification of type 2 diabetes is critical to properly control the condition and minimize the consequence. Being aware of the subtle but important symptoms might assist you to take proactive measures for your health.
The symptoms could include excessive thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, tingling or numbness in feet or hands, wounds that take time to heal, and fatigue to mention a few.
Recognizing these symptoms could help with early detection and effective management of type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes could affect other major organs, especially, blood vessels, eyes, and heart. Managing diabetes and controlling blood sugar could lower complications. Chronic complications can lead to serious damage if left unchecked. This includes:
Diabetic retinopathy arises when diabetic patients develop an eye disease. It can be diagnosed through a screening test when treated it can help to prevent eyesight loss.
Having high blood sugar levels over an extended length of time might damage your blood vessels. This can occasionally result in heart attacks and strokes.
Diabetes could damage your kidney in the long run making it hard to filter out waste out of your body. You will have visible symptoms like swollen ankles, and feet, blood in urine, and feeling sick and shortness of breath.
If untreated, foot problems could lead to amputation. Nerve damage can impair feeling in your feet, and high blood sugar levels can affect circulation, causing sores and wounds to heal slower than usual.
Your doctor may want to check your blood pressure and cholesterol levels since diabetes increases your risk of cardiovascular disease. If you have heart disease symptoms, you may require further tests.
Lifestyle changes and diet could help in managing type 2 diabetes. If lifestyle modifications alone aren't enough to bring you to your goal blood sugar levels, you may need to take medication.
Consult with the best diabetologist to stick to a diet plan to reduce your blood sugar level. Focus on lowering your carbs and sugar intake, adding more veggies and fruits. Food that contains a lot of fiber is an ideal option.
Aim for 150 minutes or more of moderate to intense aerobic activity each week, such as brisk walking, biking, jogging, or swimming. Sitting still for a long period could increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
When you are overweight, losing weight in a healthier way is a must.
Depending on your therapy, particularly if you're on insulin, your physician will advise you on when and how frequently you should test your blood sugar levels.
A long-term health condition could worsen your mental illness. Whether you are diagnosed with diabetes or have had it for some time, work with your doctor to prevent further complications.